A very common task in data analysis is that of grouping a set of objects into subsets such that all elements within a group are more similar to them than they are to the others. The practical applications of such a procedure are many: given a medical image of a group of cells, a clustering algorithm could aid in identifying the centers of the cells; looking at the GPS data of a user’s mobile device, their more frequently visited locations within a certain radius can be revealed; for any set of unlabeled observations, clustering helps establish the existence of some sort of structure that might indicate that the data is separable.
Mathematical background
The k-means algorithm takes a data set X of N points as input, together with a parameter K specifying how many clusters to create. The output is a set of K cluster centroids and a labeling of X that assigns each of the points in X to a unique cluster. All points within a cluster are closer in distance to their centroid than they are to any other centroid.
The mathematical condition for the K clusters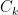 and the K centroids
and the K centroids  can be expressed as:
can be expressed as:


The two-step procedure continues until the assignments of clusters and centroids no longer change. As already mentioned, the convergence is guaranteed but the solution might be a local minimum. In practice, the algorithm is run multiple times and averaged. For the starting set of centroids, several methods can be employed, for instance, random assignation.
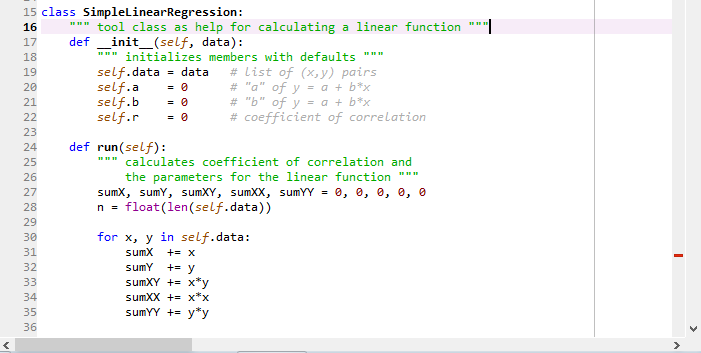
Below is a simple implementation of Lloyd’s algorithm for performing k-means clustering in python:
The k-means algorithm takes a data set X of N points as input, together with a parameter K specifying how many clusters to create. The output is a set of K cluster centroids and a labeling of X that assigns each of the points in X to a unique cluster. All points within a cluster are closer in distance to their centroid than they are to any other centroid.
The mathematical condition for the K clusters
Minimize  with respect to
with respect to  .
.
Lloyd’s algorithm
Finding the solution is, unfortunately, NP hard. Nevertheless, an iterative method known as Lloyd’s algorithm exists that converges (albeit to a local minimum) in few steps. The procedure alternates between two operations. (1) Once a set of centroids  is available, the clusters are updated to contain the points closest in distance to each centroid. (2) Given a set of clusters, the centroids are recalculated as the means of all points belonging to a cluster.
is available, the clusters are updated to contain the points closest in distance to each centroid. (2) Given a set of clusters, the centroids are recalculated as the means of all points belonging to a cluster.
The two-step procedure continues until the assignments of clusters and centroids no longer change. As already mentioned, the convergence is guaranteed but the solution might be a local minimum. In practice, the algorithm is run multiple times and averaged. For the starting set of centroids, several methods can be employed, for instance, random assignation.
Below is a simple implementation of Lloyd’s algorithm for performing k-means clustering in python: